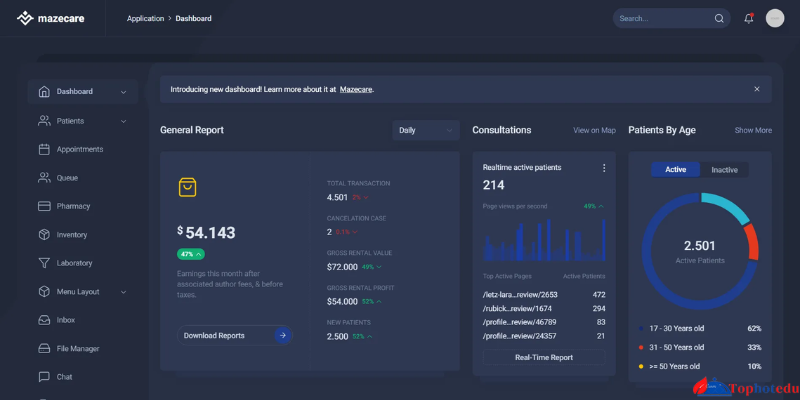
In the fast-paced world of healthcare, the efficient management of patient information is paramount. Patient management software has emerged as a revolutionary tool in healthcare facilities, offering streamlined processes, enhanced patient care, and improved outcomes. This comprehensive guide aims to delve into the intricate workings of patient management software, exploring its features, benefits, challenges, and future prospects.
Contents
Understanding Patient Management Software

Patient management software, also known as electronic health record (EHR) or electronic medical record (EMR) software, is a digital platform designed to centralize and manage patient information efficiently. It encompasses a wide range of functionalities, including patient demographics, medical history, laboratory results, medication records, appointment scheduling, billing, and more.
Key Features
- Centralized Patient Records: Patient management software consolidates all patient information into a centralized database, accessible to authorized healthcare professionals. This eliminates the need for paper-based records, reducing errors and enhancing data security.
- Appointment Scheduling: Advanced scheduling features enable healthcare providers to manage appointments seamlessly. Patients can book appointments online, receive reminders, and reschedule if necessary, improving clinic efficiency and patient satisfaction.
- Medical Billing and Claims Management: Integrating billing and claims management functionalities simplifies the billing process for healthcare facilities. Automated billing ensures accurate invoicing and timely reimbursement, reducing administrative burden and optimizing revenue cycles.
- Clinical Documentation: Patient management software facilitates comprehensive clinical documentation, allowing healthcare providers to record patient encounters, diagnoses, treatments, and progress notes electronically. This enhances communication among healthcare team members and ensures continuity of care.
- Interoperability: Interoperability is a crucial feature that enables seamless exchange of patient data between different healthcare systems and providers. Integration with external systems, such as pharmacies and laboratories, streamlines workflows and improves care coordination.
- Decision Support Tools: Built-in decision support tools offer clinical guidance based on evidence-based medicine, helping healthcare providers make informed decisions and improve patient outcomes. These tools may include drug interaction alerts, clinical guidelines, and diagnostic support.
Benefits of Patient Management Software

- Improved Efficiency: By automating routine tasks and streamlining workflows, patient management software enhances the efficiency of healthcare facilities. Healthcare providers can devote more time to patient care rather than administrative tasks.
- Enhanced Patient Care: Access to comprehensive patient information empowers healthcare providers to deliver personalized and evidence-based care. Timely access to medical records and decision support tools improves diagnostic accuracy and treatment outcomes.
- Cost Savings: Patient management software reduces operational costs associated with paper-based record-keeping, transcription errors, and administrative overhead. It also optimizes revenue cycles through efficient billing and claims management.
- Increased Patient Engagement: Online appointment scheduling, secure messaging, and patient portals promote active patient engagement and communication. Patients can access their medical records, review test results, and communicate with their healthcare providers conveniently.
- Data Security and Compliance: Patient management software adheres to stringent data security standards and regulations, such as HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act). Data encryption, access controls, and audit trails ensure the confidentiality and integrity of patient information.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Whether it’s a small clinic or a large hospital network, patient management software offers scalability and flexibility to accommodate diverse healthcare settings. Modular design allows customization according to specific needs and workflows.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its numerous benefits, implementing and utilizing patient management software comes with its own set of challenges and considerations:
- Initial Investment: The upfront costs associated with purchasing and implementing patient management software can be significant, especially for smaller healthcare providers. However, the long-term benefits often outweigh the initial investment.
- User Adoption: Resistance to change and unfamiliarity with new technology can impede user adoption. Healthcare providers and staff require adequate training and support to effectively utilize patient management software.
- Interoperability Issues: Achieving seamless interoperability between different healthcare systems and software platforms remains a challenge. Standardized data exchange protocols and collaboration among stakeholders are essential to overcome interoperability barriers.
- Data Security Concerns: With the digitization of patient information comes the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access. Healthcare facilities must implement robust security measures, such as encryption, access controls, and regular audits, to safeguard patient data.
- Workflow Integration: Integrating patient management software into existing workflows without disrupting clinical operations requires careful planning and customization. Workflow analysis and stakeholder input are essential for successful implementation.
- Regulatory Compliance: Healthcare facilities must ensure compliance with regulatory requirements, such as HIPAA, GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation), and other local regulations governing the use and protection of patient data.
Future Trends and Innovations

The landscape of patient management software continues to evolve with advancements in technology and healthcare delivery. Some emerging trends and innovations include:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning: AI-powered algorithms and machine learning techniques are increasingly being integrated into patient management software to automate tasks, analyze data patterns, and improve clinical decision-making.
- Telehealth Integration: The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the adoption of telehealth solutions, leading to the integration of telehealth capabilities into patient management software. Virtual consultations, remote monitoring, and telemedicine services are becoming integral components of modern healthcare delivery.
- Mobile Applications: Mobile-friendly patient management applications enable healthcare providers to access patient information and perform tasks on-the-go, enhancing flexibility and convenience. Patients can also use mobile apps to manage appointments, access health records, and communicate with their providers.
- Blockchain Technology: Blockchain technology holds promise for enhancing the security and interoperability of patient management software. By creating tamper-proof, decentralized ledgers, blockchain can ensure the integrity and privacy of patient data while facilitating secure data exchange between stakeholders.
- Predictive Analytics: Predictive analytics tools analyze large datasets to identify trends, predict outcomes, and optimize healthcare processes. These insights can help healthcare providers proactively manage patient populations, improve resource allocation, and prevent adverse events.
- Genomic Medicine Integration: Integration of genomic data into patient management software enables personalized medicine approaches based on individuals’ genetic profiles. This facilitates targeted therapies, risk assessment, and precision medicine initiatives.
Conclusion
Patient management software has transformed the landscape of healthcare delivery, offering a multitude of benefits ranging from improved efficiency and patient care to enhanced data security and compliance. Despite the challenges associated with implementation and utilization, the future of patient management software is promising, with continued innovation and integration of emerging technologies. By embracing these advancements and overcoming existing barriers, healthcare facilities can optimize workflows, enhance patient outcomes, and pave the way for a more connected and patient-centric healthcare ecosystem.